pH (potential of Hydrogen) and TDS (Total Dissolved Solids) are critical parameters that greatly influence the success of hydroponic systems. They affect nutrient availability, nutrient uptake by plants, and overall plant health. Let’s explore how pH and TDS impact hydroponics:
pH in Hydroponics:
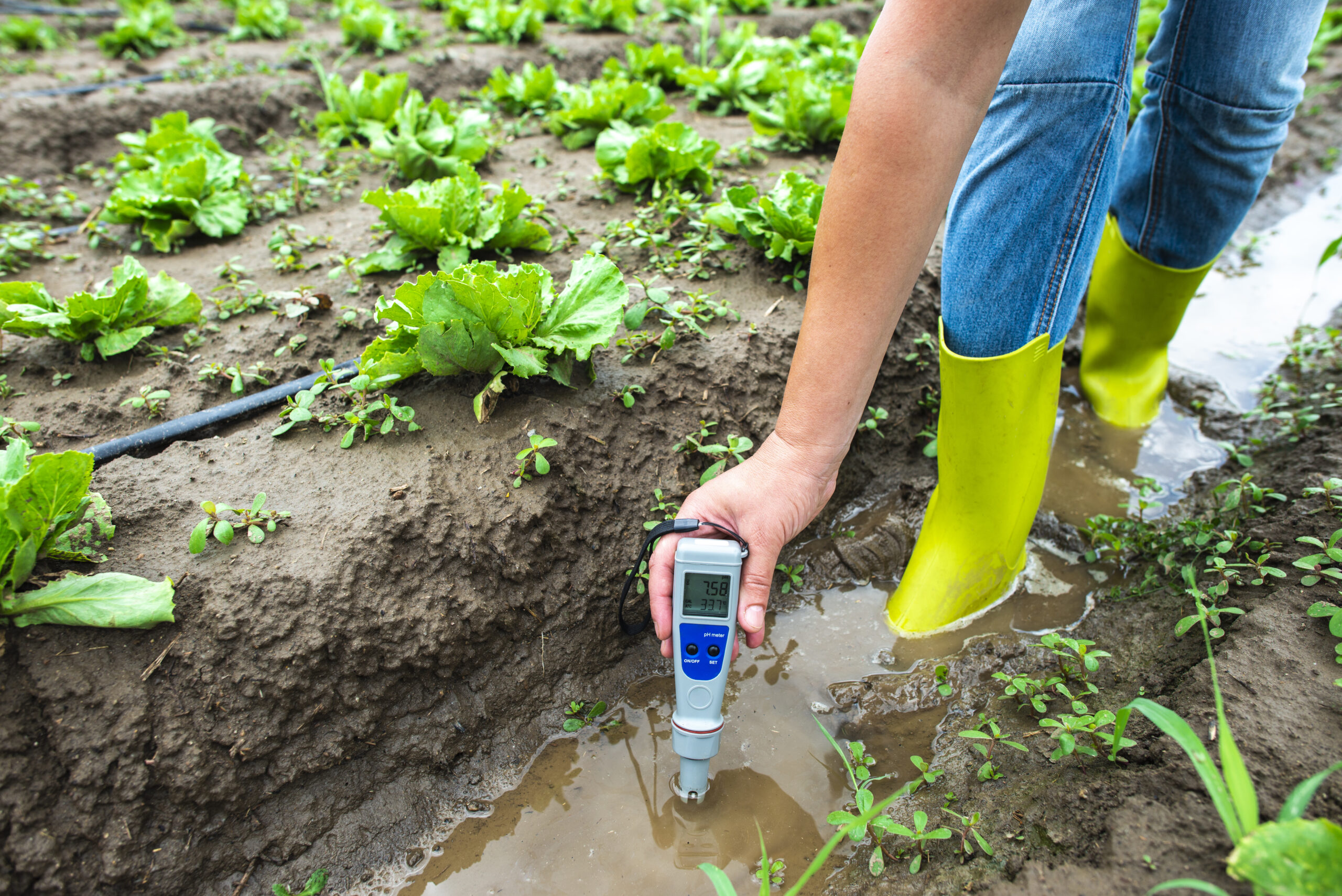
pH refers to the acidity or alkalinity of a solution, and it’s measured on a scale from 0 to 14. In hydroponics, pH is crucial because it affects nutrient solubility and availability to plants:
- Nutrient Availability: Different nutrients are available to plants at specific pH ranges. For example, certain nutrients like iron and manganese become less available at high pH levels, leading to potential deficiencies.
- Nutrient Uptake: The pH of the nutrient solution influences the ability of plant roots to take up nutrients. If the pH is too high or too low, plants might experience nutrient uptake issues even if nutrients are present in the solution.
- Plant Health: Incorrect pH levels can lead to nutrient imbalances, which can result in poor plant growth, leaf discoloration, stunted growth, and other physiological issues.
Optimal pH levels for most hydroponic crops typically fall in the range of 5.5 to 6.5. Regular pH monitoring and adjustment are essential to maintain nutrient availability and ensure that plants can efficiently absorb the required nutrients.
TDS in Hydroponics:
TDS measures the concentration of dissolved minerals, salts, and nutrients in a solution, typically expressed in parts per million (ppm) or milligrams per liter (mg/L). In hydroponics, TDS indicates the nutrient strength of the solution:
- Nutrient Concentration: TDS provides an indication of the concentration of nutrients in the solution. A higher TDS indicates a more concentrated nutrient solution.
- Nutrient Balance: Monitoring TDS helps ensure that the nutrient solution is balanced and contains appropriate concentrations of essential nutrients.
- Plant Growth: Maintaining the right TDS ensures that plants receive the necessary nutrients for optimal growth. Too low a TDS might lead to nutrient deficiencies, while too high a TDS can cause nutrient imbalances and stress.
The ideal TDS range varies depending on the plant species, growth stage, and specific hydroponic system. However, a common range is usually between 800 and 1500 ppm. It’s important to note that TDS readings need to be interpreted alongside pH levels to make accurate assessments of nutrient availability and plant health.
Regular monitoring of pH and TDS, along with timely adjustments when needed, is crucial in hydroponic systems to maintain nutrient balance, support proper nutrient uptake, and ensure healthy plant growth. Tools like pH meters and TDS meters are essential for accurate measurement and management of these parameters.